Geological studies and land management
The perpetuation of disasters and calamities caused by hydro geological instability, has prompted in recent years Government and Local Authorities to search for solutions in order to minimize the damages or at least to mitigate the effects of events that are beyond human control, focusing on the analysis of the timeframe and the circumstances of the site in which these events can occur.

The geological risk is described by a formula that links hazard, vulnerability and exposed value. The risk can be defined as:

The risk assessment is the analysis of the relationships between the various factors of vulnerability of the area and the possible types of hazard.
The mitigation measures can be implemented, case by case, by acting against the hazard, the vulnerability or the value of elements at risk.
The vulnerability depends on both the type of the element at risk and the intensity of the landslide process and describe the connection between the intensity of the phenomenon and its possible consequences.
The potential damage is not related to the probability of occurrence of the phenomenon (the hazard) and expresses the share of the value of element at risk that may be compromised in case of occurrence of the landslide.

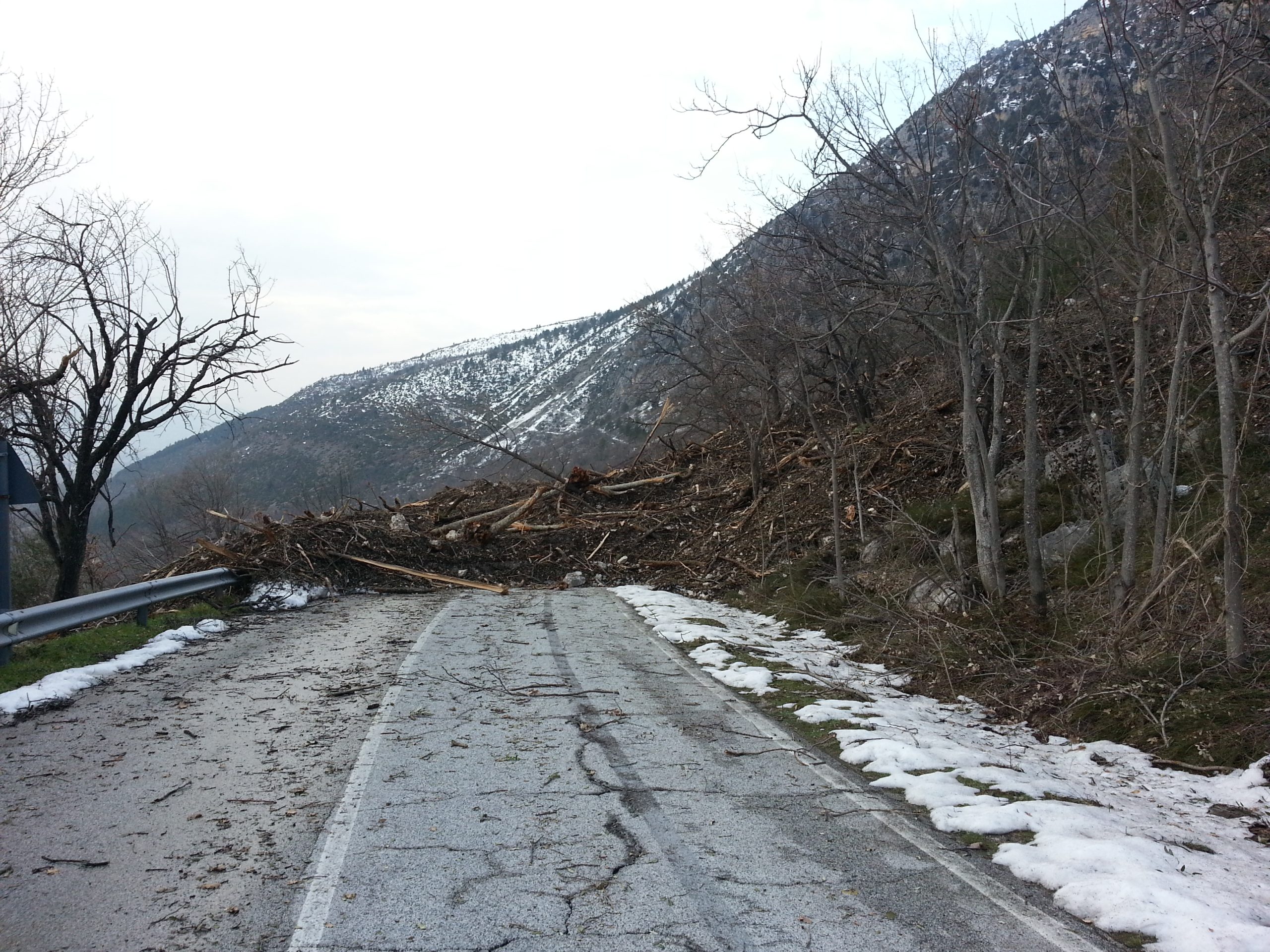
In order to measure the risks of slope instability, investigations are performed, aimed at the assessment and cartographic representation of the level of hazard associated with gravitational movements or mass movements.
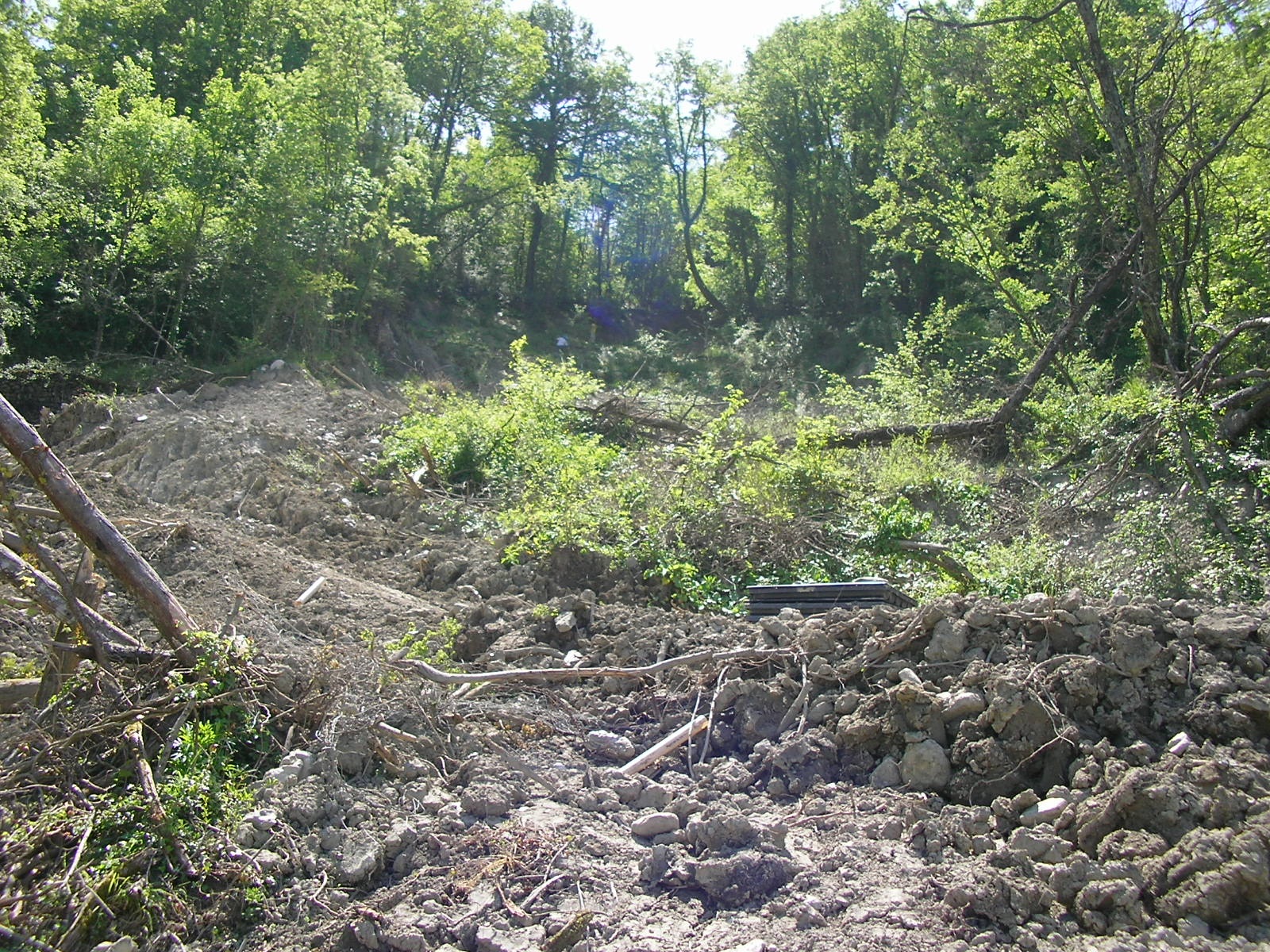
For the hazard assessment, a number of analytical documents are developed, represented by thematic maps associated with databases containing the main forecasting elements . These basic data are processed by statistical procedures or by analytical evaluation, to provide a Paper illustrating the level of hazard in the territory.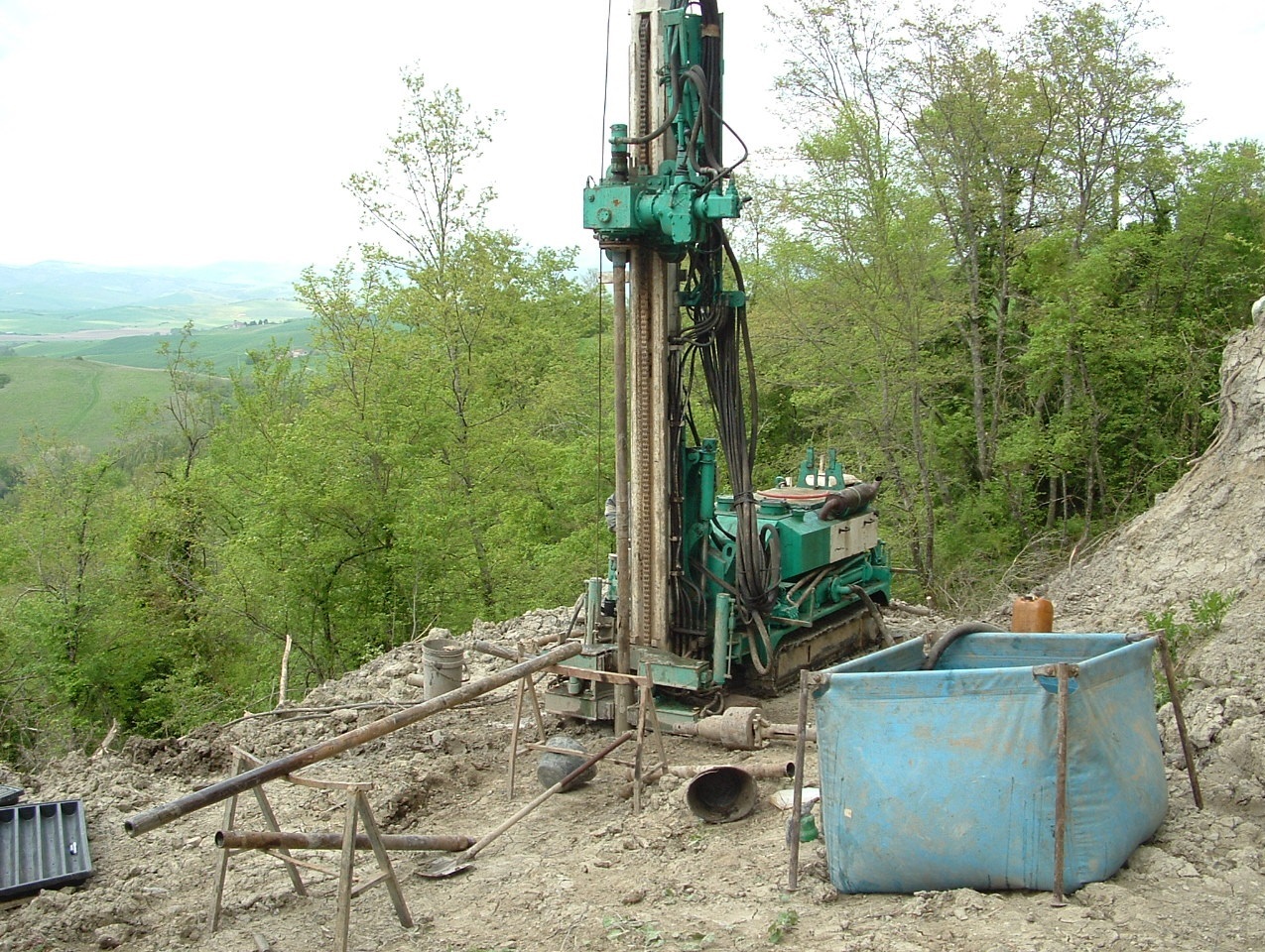
The activities and criteria to be followed during the risk assessment in a defined zone, aimed at an adequate prevention in areas subject to danger or reclamation are illustrated below:
- Research and analysis of bibliographic historical data published ;
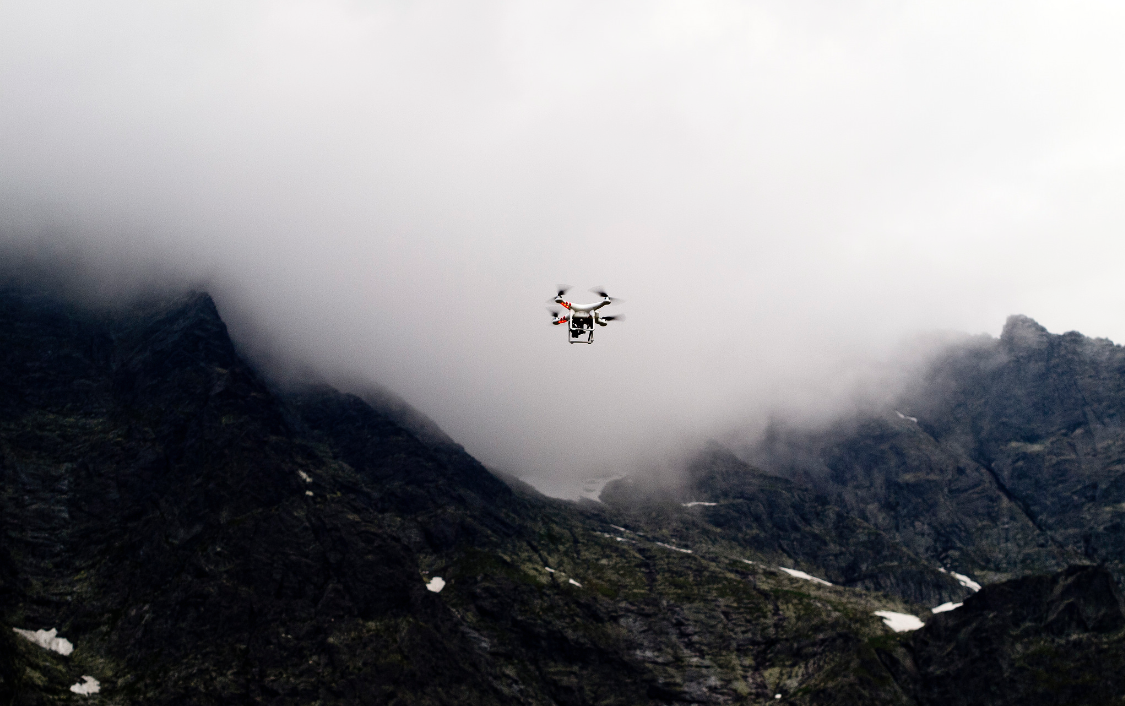
- Production of a detailed base maps through aerial surveys carried out with help of a drone;
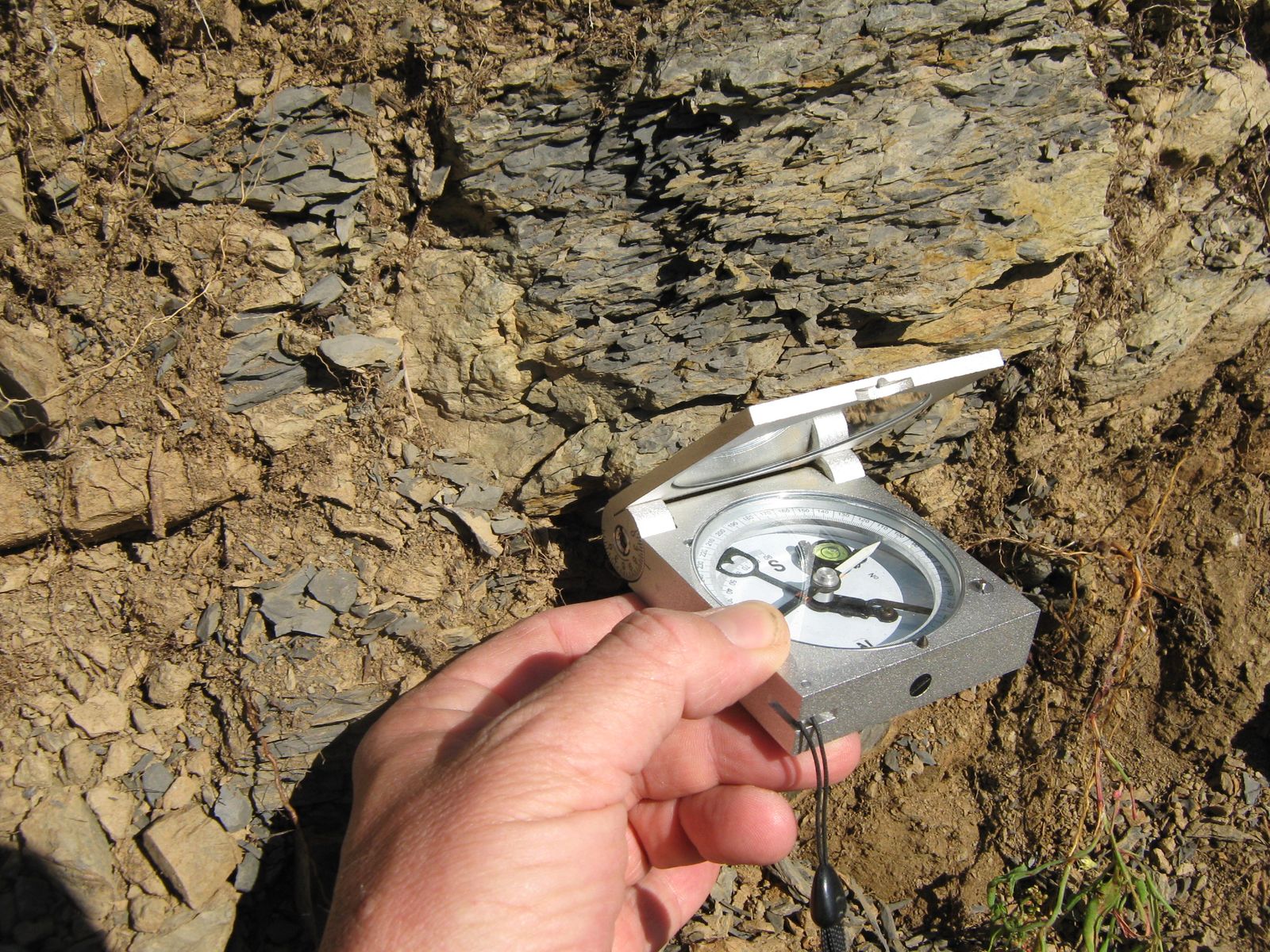
- Geological-structural, geomorphological and hydrogeological surveys;
- Geomechanical surveys;
- Planning, management and execution of geophysical surveys;
- Interpretation of experimental data obtained from field investigations.

The following final documents are developed:
• Geological-structural map, geomorphological and hydrogeological dynamic map ;
• Classification map and hazard / risk zoning ;
• Table of stratigraphic sections perpendicular to the slope;
• Geological report with geotechnical considerations of slope stability;
• Geomechanics Report ;
• Results of investigations and surveys;
• Report on studies and interventions for the protection from landslide risk;
• Report on mitigation techniques for landslide risks.
Risk prevention includes activities aimed to avoid or minimize the potential occurrence of damages caused by landslides.
Prevention activities must be planned for all areas in which the risk is socially not tolerable, with priority for high-risk areas.
Two different strategies of prevention are possible:
- risk mitigation by structural hazard mitigation;
- risk mitigation by non-structural measures to reduce the potential damage.
The assessment of their effectiveness in terms of risk reduction and the programming of any additional interventions are parts of Forecast and Prevention Provincial, Regional Plan and Special Areas, foreseen by National Laws.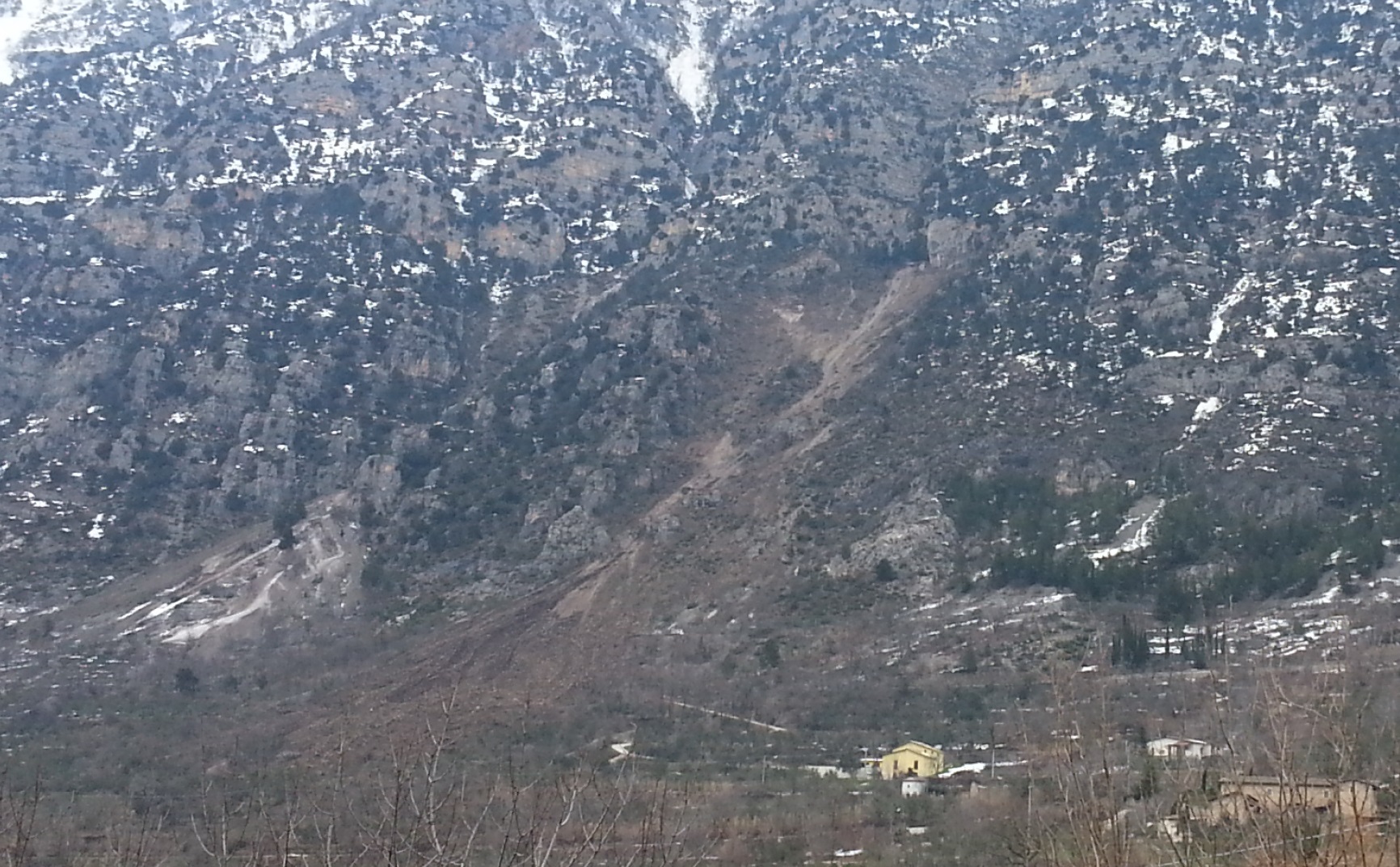
The strategy of the plan must coincide with design phase and selection of appropriate preventive measures against dangerous natural processes: it is essential the knowledge of the dynamics of the events and the possible effects on settlements and infrastructures.
Mitigation actions that can be implemented are effective only when applied based on the fulfillment of a specific regulation applied to construction and urban planning, which may foreseen the appropriate protective measures in dangerous areas.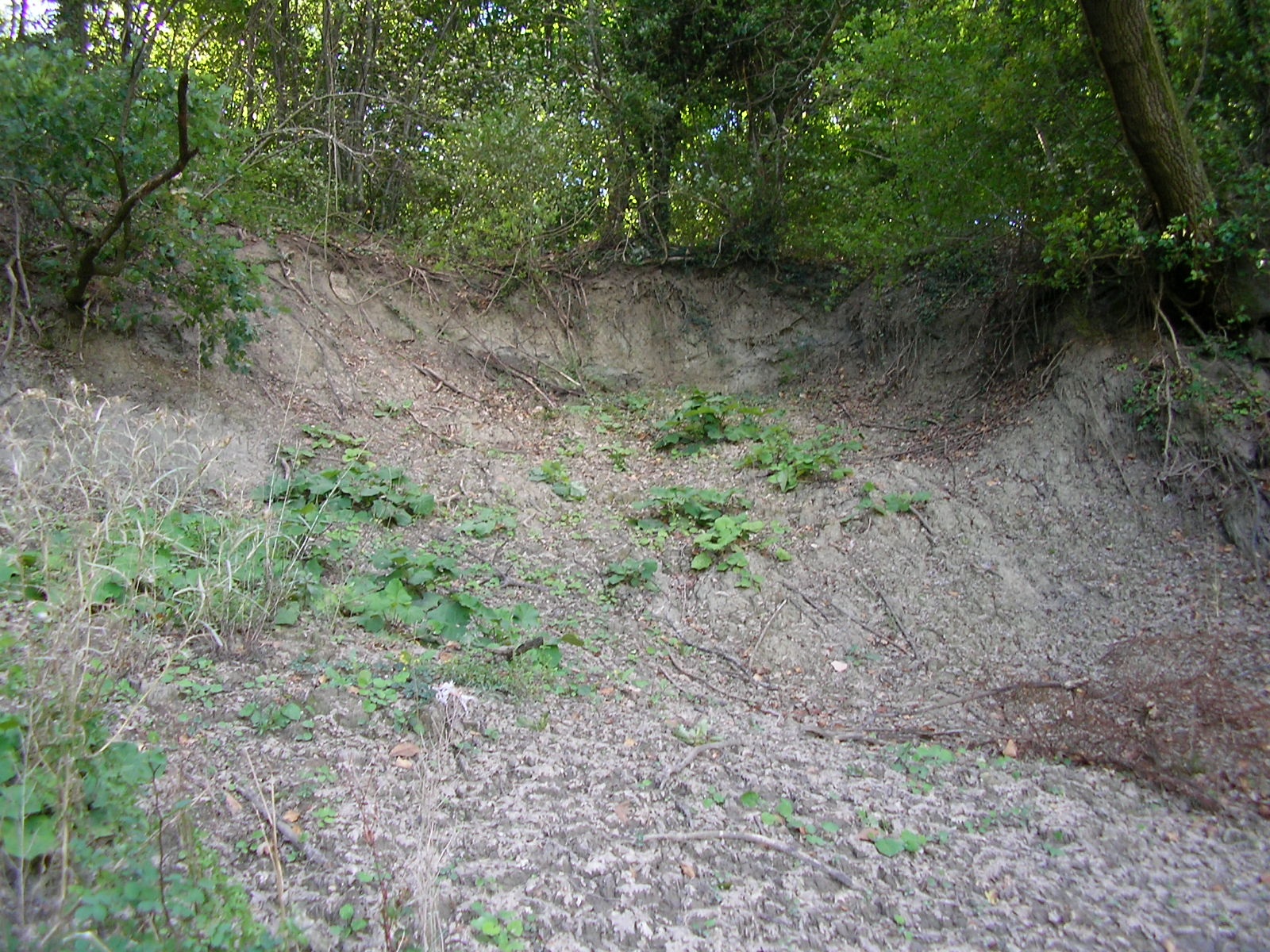
-
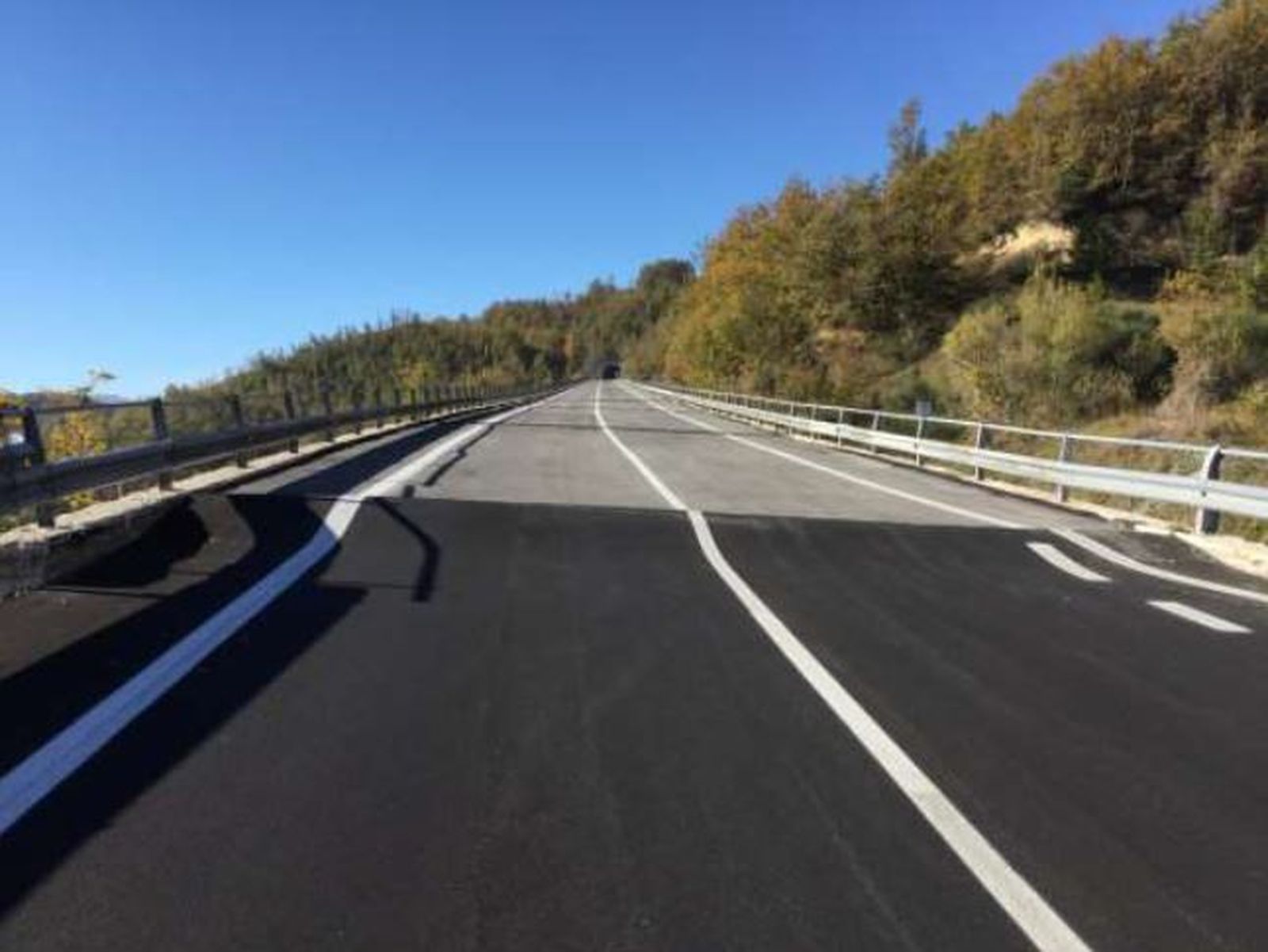 Road repair plan S.S. 685 – ANAS MARCHESettore: Roads & Highways
Road repair plan S.S. 685 – ANAS MARCHESettore: Roads & Highways -
 Tornolo (PR) 220-kV Electrical SubstationSettore: Energy Infrastructures
Tornolo (PR) 220-kV Electrical SubstationSettore: Energy Infrastructures -
 Vatovavy Fitovinany Dams – MadagascarSettore: Ports and hydraulic projects
Vatovavy Fitovinany Dams – MadagascarSettore: Ports and hydraulic projects -
 220 kV Austria – Italy InterconnectionSettore: Energy Infrastructures
220 kV Austria – Italy InterconnectionSettore: Energy Infrastructures -
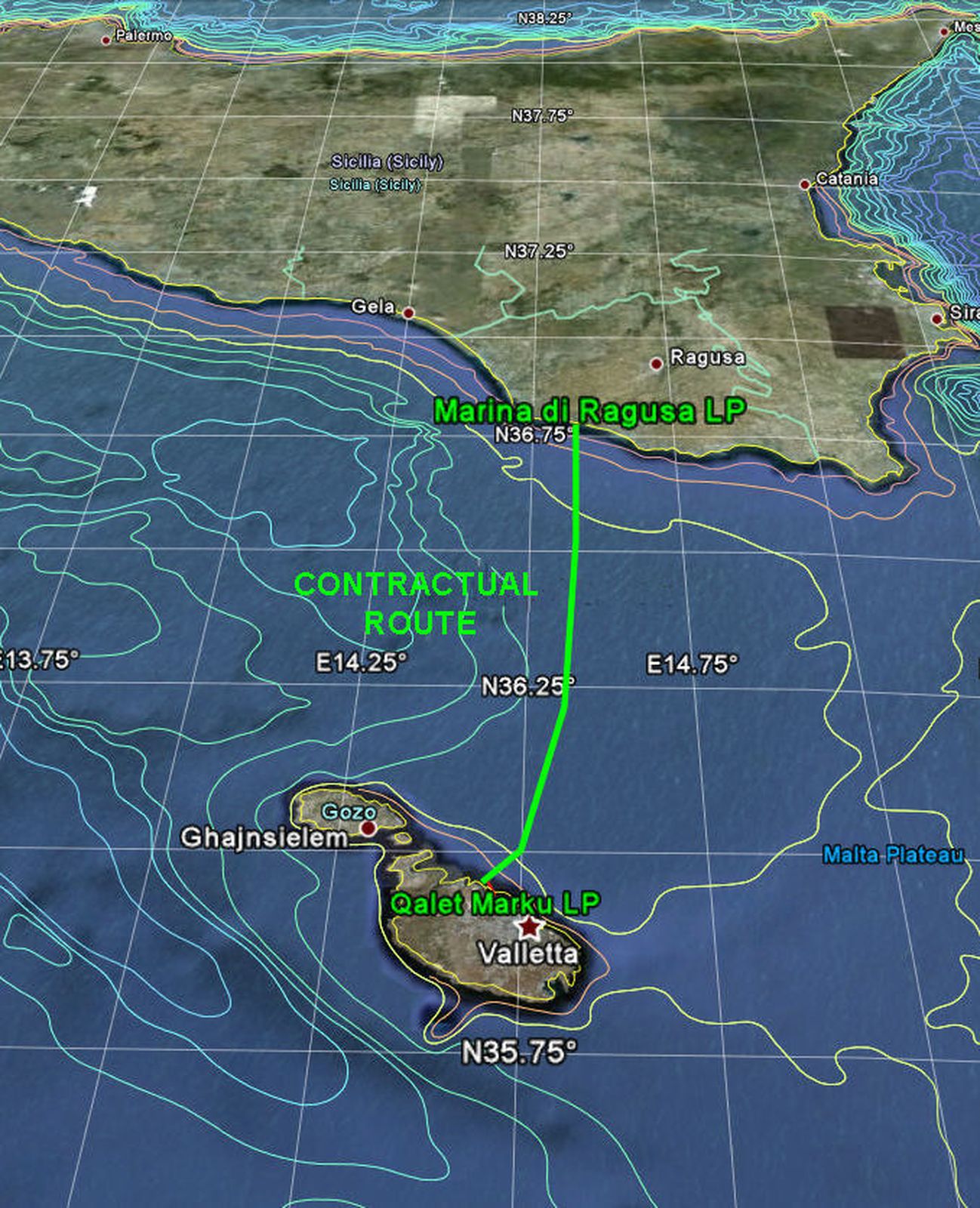 220 kV Italy – Malta submarine interconnector – EISSettore: Energy Infrastructures
220 kV Italy – Malta submarine interconnector – EISSettore: Energy Infrastructures -
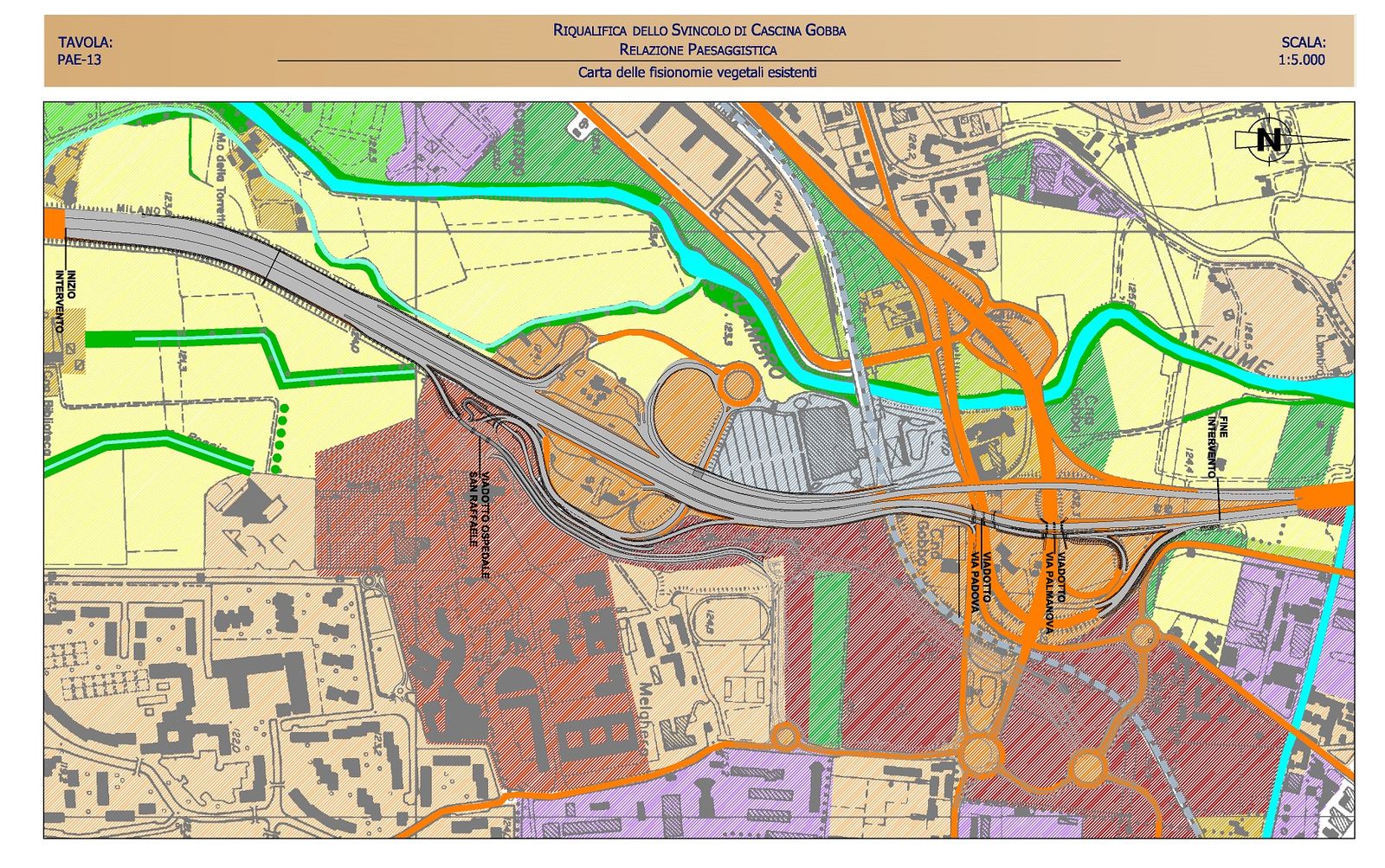 A51 Milan Eastern Ring Road – junction of Cascina GobbaSettore: Roads & Highways
A51 Milan Eastern Ring Road – junction of Cascina GobbaSettore: Roads & Highways -
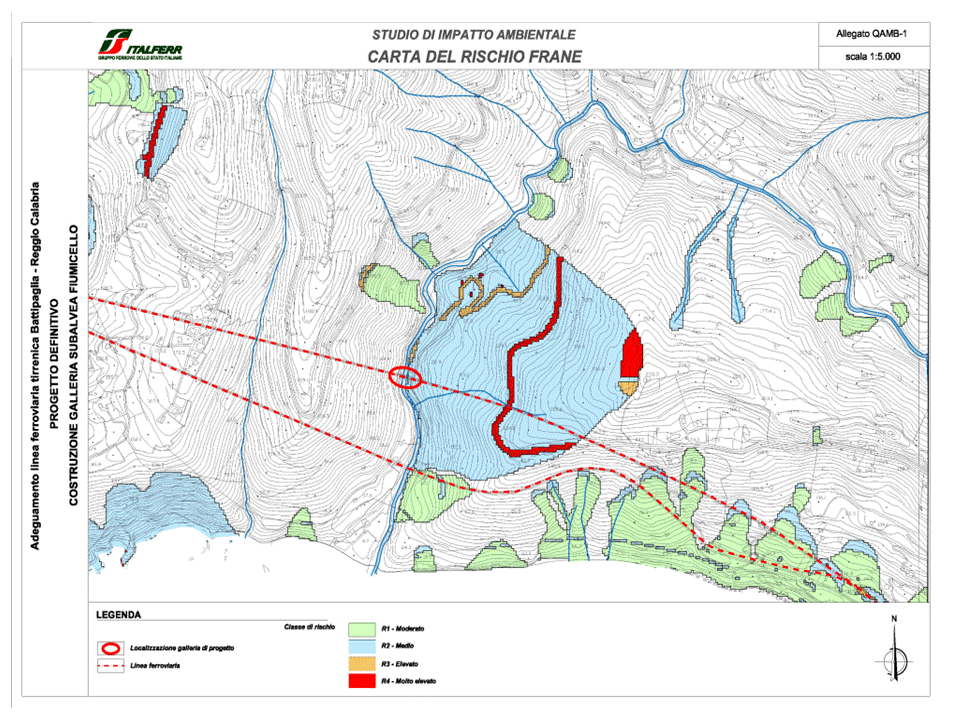 Battipaglia-Reggio Calabria Railway – Fiumicello TunnelSettore: Railways & Station
Battipaglia-Reggio Calabria Railway – Fiumicello TunnelSettore: Railways & Station -
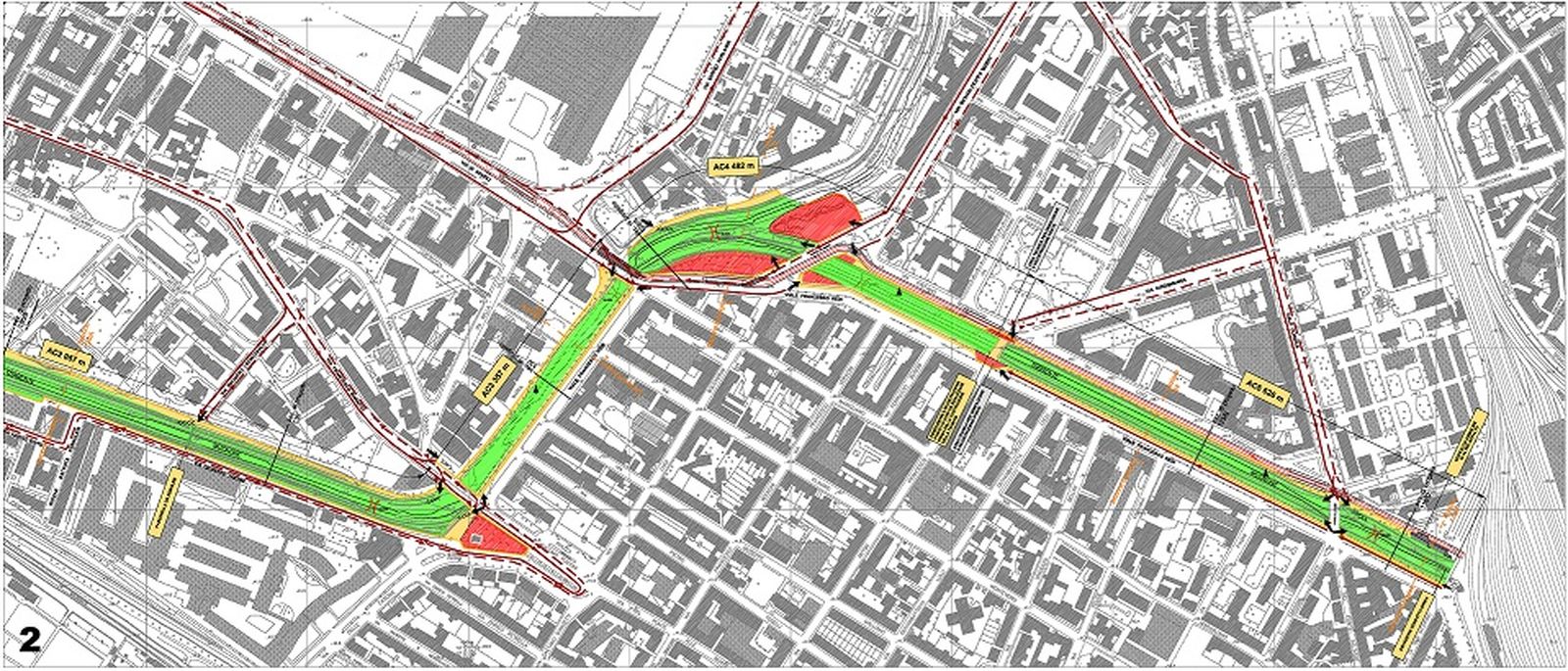 Hydraulic adjustment of Mugnone Stream – FlorenceSettore: Railways & Station
Hydraulic adjustment of Mugnone Stream – FlorenceSettore: Railways & Station